
E-services
- Categories Computer Systems, E-Services
E-Mail & FTP

Q 1. What is Email (Electronic Mail)?
Ans:
E-Mails are messages distributed by electronic means from one computer user to one or more recipients via a network.
e.g.Web based – Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo Mail,
E-mail clients – Mozilla Thunderbird, Postbox Express, eM.
Q 2. What is the structure of E-Mail?
Ans:
E-Mails typically has following structure.
- FROM: This is the address of the sender of the e-mail. Along with address the display name is also showcased.
- TO: This is the address of the receiver to whom the mail is sent.
- CC: CC stands for Carbon Copy. These are list of people who also receive a copy of the message. This list is visible to receiver
- BCC: BCC is for Blind carbon Copy. These are list of people who also receive a copy of the message. This list is NOT visible to TO and CC receivers.
- SUBJECT: A short title for the mail.
- BODY: The actual message being delivered
- ATTACHMENTS: You can attach one or more pictures and documents or any other with your e-mail.
- DATE: This is the date and time on which the message was sent from the sender’s computer.
- MESSAGE-ID: Every message will have a unique id, which is used to track replies to it. This is used internally by the e-mail system.
Q 3. What are Email formats?
Ans:
There are 2 main E-Mail formats.
- Plain text (.txt): Can be read by anyone, regardless of the e-mail application they use.
Does not offer any text formatting options.
- Plain text (.txt): Can be read by anyone, regardless of the e-mail application they use.
- Rich text format (.rtf) : Allows text formatting options , and inserting pictures and graphics. It cannot be read by all e-mail application.
Q 4. What are protocols used in e-mail?
Ans:
Below are some of the key E-Mail protocols.
- IMAP Protocol: IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) is a standard client/server protocol for accessing e-mail from local server. It works well over slow connections and low data transfer.
- POP3 Protocol: The POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3) protocol provides a simple, standardized way for users to access mailboxes. It download messages to their computers in one shot to minimize internet costs.
- SMTP Protocol: The SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) protocol is used ONLY when you send email to another email users (the recipient).
- HTTP Protocol: The HTTP protocol is not a protocol dedicated for email communications, but it can be used for accessing mailbox.
Q 5. What are different Email etiquettes to be used?
Ans:
Below are some of the e-mail etiquettes which we should follow
- Be concise and to the point: Do not make an e-mail longer than it needs to be.
- Use proper grammar & layout: Since reading from a screen is more difficult than reading from paper, the grammar, structure and lay out is very important for e-mail messages.
- Case Sensitivity: IF YOU WRITE IN CAPITALS IT SEEMS AS IF YOU ARE SHOUTING.
- Minimize abbreviations and emoticons: In business e-mails, use of abbreviations and emoticons (smiley faces) is generally inappropriate.
- Add an e-mail disclaimer: Disclaimers in your mails can help you from liability.
- Gender Sensitivity: If you are writing to a person unknown to you, your email should be gender neutral.
Q 6. What are mail servers?
Ans:
computer that are dedicated to processing and directing email.
Q 7. What are pros and cons of E-Mails?
Ans:
PROS:
- Sending an email is much less expensive and more faster than sending postal mail
- Unlike a telephone or in-person conversation, email by its nature creates a detailed written record of the communication
- Email allows each participant to work as per their schedule independently
CONS:
- It leads to Information overload which could lead to reduced productivity.
- The users are exposed to SPAM which is unsolicited bulk email.
- Email spoofing occurs when the email message header is designed to make the message appear to come from a known or trusted source
- Email bombing is the intentional sending of large volumes of messages to a target address leading to mail server crash
- Flaming occurs when a person sends a message (or many messages) with angry or antagonistic content.
- “email fatigue”, email bankruptcy is when a user ignores a large number of email messages after falling behind in reading and answering them
- There are various types of email scams, including advance-fee scam “Nigerian letters”, to phishing, email worms etc.
Q 8. What is FTP?
Ans:
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is network protocol used for the transfer of files between a client and server on a computer network. Secure version of FTP which is encrypted is called FTPS. FTP works over TCP/IP protocol.
e.g. Filezilla, SmartFTP, FireFTP etc.
Q 9. What is FTP Server and FTP client?
Ans:
FTP server is a computer that is running FTP server software. An FTP server listens on the network for connection requests from other computers.
FTP client is a computer that is running FTP client software. An FTP client computer initiates a connection to the server.
E-Shopping

Q 1. What is e shopping ?
Ans:
Online shopping is a form of electronic commerce in which consumers directly buy goods or services from a seller over the Internet using a web browser. It can be business-to-consumer (B2C) when a person buys from online retailer as end consumer or it can be business-to-business (B2B) where a business buys for another business.
Q 2. What are PROS and CONS of online shopping?
Ans:
PROS:
- It saves time and effort and as it offers convenience of shopping at home.
- Wide variety / range of products are available with detailed information that can be used to compare across brands.
- There are good discounts and lower prices due to elimination of maintenance and real-estate cost.
CONS:
- Lack of touch-feel-try creates concerns over the quality of the product on offer.
- Personal attention to customers and help in purchasing goods is missing
- There are concerns of frauds in online shopping which deters online buyers.
E-Learning

Q 1. What is e-Learning?
Ans:
e-Learning is learning conducted via electronic media, typically on internet, to access educational curriculum outside of a traditional classroom.
e.g
Application Areas – Classrooms, courses, Assessments, simulation or game based learning or MOOC (Massive Open Online Course) for massive audience.
Q 2. What are Pros and Cons of e-Learning?
Ans:
PROS:
- It is flexible as learning can take place anytime and anywhere.
- It helps in consistent delivery and reduces any errors due to different instructors.
- It reduced overall cost as it is less expensive to produce and can reach large number of people.
- Use of multimedia has ensured that learning is interactive.
CONS:
- Learners need to invest in technology with devices which are compatible and internet connection or power reliability
- Some learners may not be comfortable using computers
- With no fixed schedule or routine, it can become difficult for people to motivate themselves to meet specific deadlines or goals.
E-Groups

Q 1. What are e- Groups?
Ans.
- An e group refers to an online community where people post on topics of common Interest
- All posts are listed together on a discussion board , which is viewable to all the members of the group.
e.g. Google groups, Yahoo Groups.
Q 2. What are the Pros and Cons of e –Groups?
Ans:
PROS:
- They are accessible 24/7
- Encourages everyone to participate
- discussions can be revisited and can be stored for a long time
CONS:
- No physical cues leading to misunderstandings at times. One member cannot see the facial expressions or gestures of another member.
- It is hard to follow the logical sequence of discussion when it is broken by users not sticking to the topic thread.
- Many times there is information overload if there is large volume of information posted.
E-Governance
Q 1. What is e-governance?
Ans:
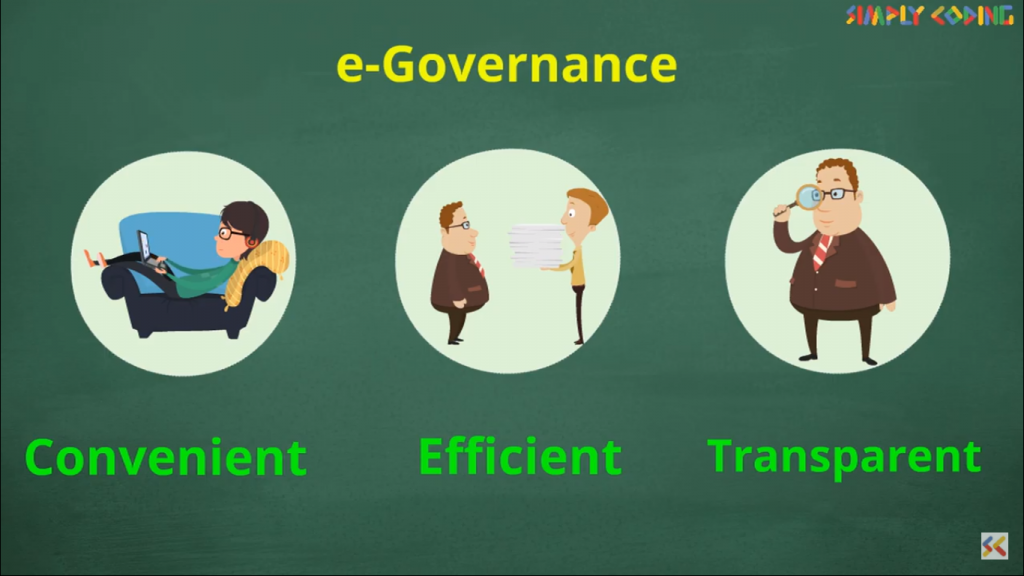
E-governance, is when government services are made available to citizens in a convenient, efficient, and transparent manner. It could be government-to-citizen (G2C), government-to-business (G2B), government-to-government (G2G) or government-to-employees (G2E) .
e.g e-Panchayat, BHIM, Ebiz, GSTN, PSP and other portals and mobile apps launched by the government under Digital India initiative.
Q 2. What are pros and cons of e-governance?
Ans:
PROS:
- It improves the efficiency of the current system (Paper based system). That would in return same money and time.
- It brings in transparency and accountability.
- Business and citizens can obtain information at a faster speed
CONS:
- It might not reach many users including those who live in the remote areas, have low literacy levels and exist below poverty line incomes.
- It could potentially lead to a lack of privacy for civilians
- There is vulnerability due to cyber attacks and security concerns.
E-Banking
Q 1. What is e-Banking (online Banking, Virtual Banking, Internet Banking)?
Ans:
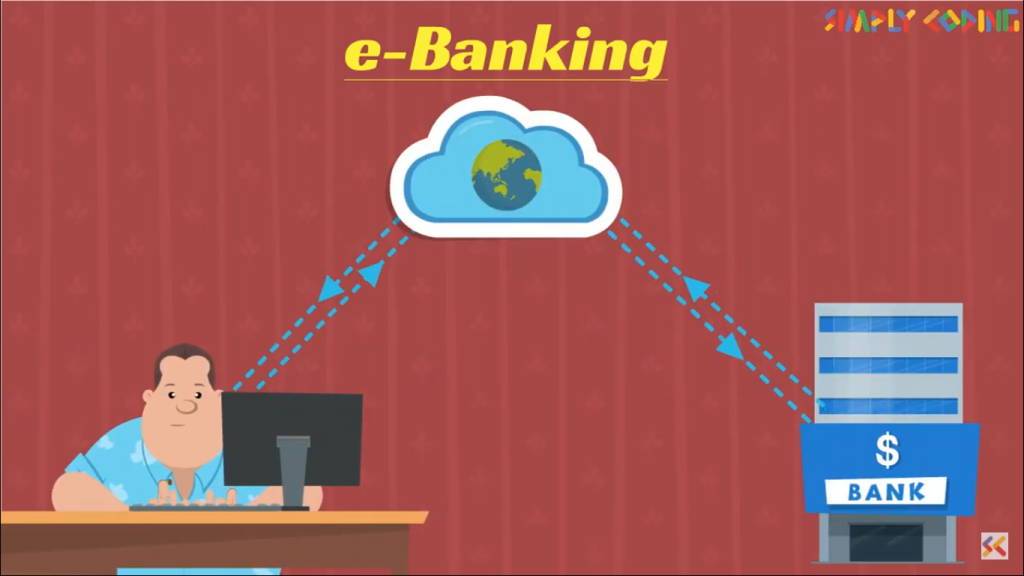
Availing the banking services through electronic meaning via internet is called e banking. A customer may perform banking transactions electronically without visiting a brick and mortar institution.
Q 2. What is mobile banking?
Ans:
Mobile banking is an Internet base service that allows one to use banking services safely and conveniently using a mobile phone or tablet.
Q 3. What are pros and cons of using mobile/Internet banking?
Ans:
PROS:
- It provides comfort and convenience to bank from anywhere 24/7
- It is cost effective as it saves time and money to travel to banks and saves paper etc. by doing payments etc. online.
- It is efficient as payments can be done instantaneously via NEFT, MIPS etc.
CONS:
- There are security concerns as online banking is targeted by hackers.
- Need for physical copies for tax authorities etc. can be a deterrent in using online banking.
- There is a lack of personal contact with bank officials which comes in useful for right financial advice.
E-Reservation

Q 1. What is e-reservation (e-booking)?
Ans:
It is reservation made online, either by email or through a website. It can be for travel, hotel, sport events, movies etc. It can be Live, means reservation made on the spot or it can be non live or offline where websites liaise with agents, hotels etc. to confirm the booking.
e.g makemytrip.com, pepperfry.com, yatra.com, bookmyshow.com etc.
Q 2. What are pros and cons of e-reservation?
Ans:
PROS:
- Online booking saves time and reduces phone time.
- It leads to businesses being available 24×7 and faster payments
- It helps to get good analytics to plan. For e.g. inventory for future.
CONS:
- It might come with a cost as there might be additional booking charges.
- It requires internet access
- There could be issues due to cancellations, returns or sudden surge in orders etc.
Blogs

Q 1. What are blogs?
Ans:
A blog (shortening of “weblog”) is an online journal or informational website displaying information in the reverse chronological order,.
A person who writes and maintains a blog is called blogger and art of writing a blog is called blogging.
Microblogging is a type of blogging featuring very short post.
Q 2. Explain Advantages and Disadvantages of Blogs
Ans:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Enables you to write down your thoughts on anything that interests you. | Whatever you publish is available for everyone to see. If you write a post in anger you might regret later. |
| Easy to set up; don’t need much technical knowledge. | Personal blogs may be biased or contain inaccurate information. |
| Easy and quick to update or add new posts. | Blogs can be time-consuming. Finding time to write regular updates can become a chore. |
| People can leave comments on your blog. | People may leave rude or inappropriate comments. |
| If you want to read other people’s blogs there are literally millions to choose from. | There are many very dull blogs around. You may have to look at many before you find some worth reading. |
Online Chat

Q 1. What is Online Chat?
Ans:
Online chat may refer to any kind of communication over the Internet that offers a real-time transmission of text messages from sender to receiver.
Q 2. What is chat room?
Ans:
A chat room is part of a website or an online servicethat provides a venue for communities of users with a common interest to communicate in real time
Q 3. What are different types of Chat?
Ans:
- Instant Messaging (IM): This initially originated as only text based messaging with AOL being the most popular one. Today, most instant messaging takes place on messaging apps such as WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, WeChat, and Viber.
- I seek You (ICQ): It used a proprietary protocol and needs ICQ client to be downloaded. Now it has included all features such as social networking, video conferencing etc.
- Internet Relay Chat (IRC): The chat process works on a client/server networking model and needs a client to be installed. It has features to chat in groups and individual and also to transfer files.
- Web Based Chat: This allows users instantaneous access and only a web browser is required to chat.
Social Networking

Q 1. What is Social Networking?
Ans:
Social networking is the use of internet-based social media programs to make connections with friends, family, classmates, customers and clients.
e.g. Facebook, Google+,LinkedIn, twitter
Features offered – Mails, Messaging, Blogs, Photo Albums, Walls, Groups etc.
PROS:
- It helps to stay connected with friends and families and find and connect with people that share the same interests.
- It works as an Invaluable Promotional Tool by which people can promote and market themselves
- Information can be spread quickly
CONS:
- It sometimes perpetuates false and unreliable Information which can cause panic.
- It is leading to Cyber Bullying/Trolling wherein people are publicly harassing one another, and posting mean or slanderous things which are broadcast-ed to the entire cyber world
- People are becoming more and more addicted to using it.
Web Browsers and Web Addresses
Q 1. What are Web Browsers?
Ans:
It is program or software on a client computer that retrieves information from the web. Examples are: Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Mozilla FireFox, Netscape, Mosaic, Opera, Safari, Lynx etc.
Q 2. What is a URL?
Ans:
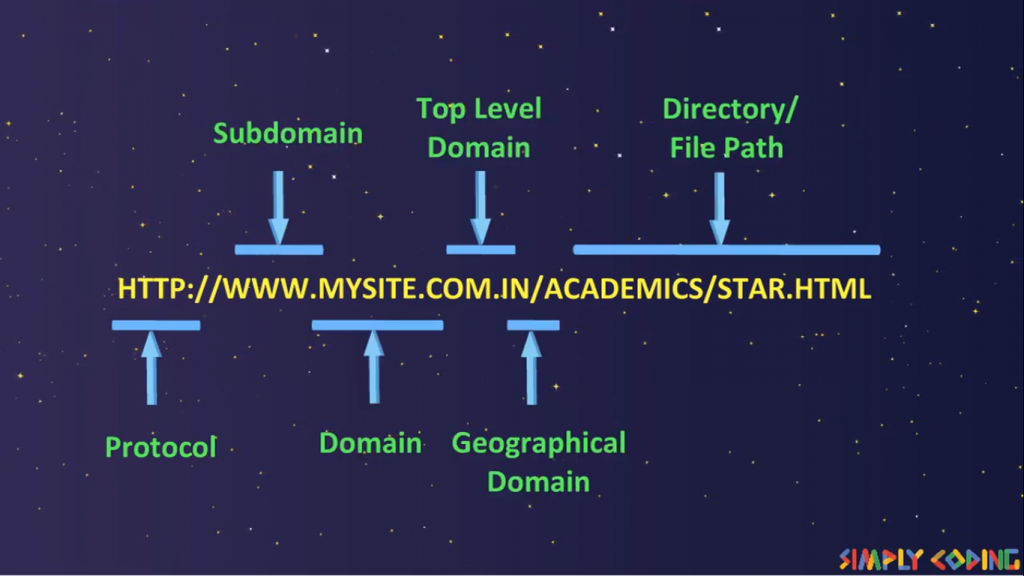
Uniform Resource Locator is also called as web address. It gives
- The protocol used to access it.
- Location of a resource on the internet
Typical format is : protocol://domain/other_info
e.g. http://www.google.com/index.html
Q 3. What are Protocols?
Ans:
A protocol is a system of rules that defines how something is to be done. In computer terminology, a protocol is usually an agreed-upon or standardized method for transmitting data and/or establishing communications between different devices.
Q 4. What are different types of protocols used on the internet?
Ans:
Internet uses multiple protocols. Some of the more common ones are
| Protocol | Description |
|---|---|
| TCP/IP | Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol – Used to transfer data in packets across the network. |
| HTTP | Hypertext Transfer Protocol are set of rules for transferring files (text, graphic images, sound, video, and other multimedia files) on the World Wide Web |
| Telnet | Used for remote login to any computer on network |
| FTP | File Transfer Protocol is used to transfer files over the net |
Q 5. What is Domain name?
Ans:
A domain name is the address where Internet users can access your website.Any name registered with the DNS is a domain name. Domain names are organized into subdomains in hierarchical fashion. E.g. of top level domains are.
- Com – Commercial
- Edu – Educational
- Gov – Government
- Mil – Military
- Net- Network resource
- Org – Non profit organization
- Co – Company
- Tv – Television
Q 6. What is DNS?
Ans:
Domain Naming System is the phone book of internet. It translates domain names to IP addresses so browsers can load Internet resources.
Q 7. How does Search Engine Work?
Ans:
A search engine work with help of following 3 elements
- Spiders or Webcrawler: Search engines use a software called spider or webcrawler or Robot or agent which scour the Internet looking for documents and their web address. They crawl from one server to another, compiling huge lists of URLs
- Indexing Software and Database: The indexing software extracts information from the documents and web addresses, prepares an Index of it and stores in a database.
- Search Algorithm: When a user enters keywords to search, the search engine software searches its database using a unique search method called search algorithm. It then displays the result of matching documents or web addresses.
Q 8. What are some common ways to frame search queries?
Ans:
Below are few common ways
- Sentence as Single Phrase:Surround your query in quotes or put some punctuation marks (; or -) if you want it to be treated as single phrase
- Wild card:Use wildcard *for pattern matching.
- Case sensitive:The lowercase word matches are not case-sensitive but uppercase words are case-sensitive.
- + sign: To specify that a word or phrase must appear in matched document, put a plus sign (+) immediately before it.
- –ve sign:To specify that a word or phrase must not appear in matched documents, put a minus sign (-) immediately before it.
You may also like

E-Commerce and E-Governance: Question Bank

Internet and WWW: Question Bank

