Implementing Stack using Array in Java
- Categories Java, Data Structures
To understand more about Stack watch our video on Implementing Stack using Array in Java – click here
Q. What is a stack?
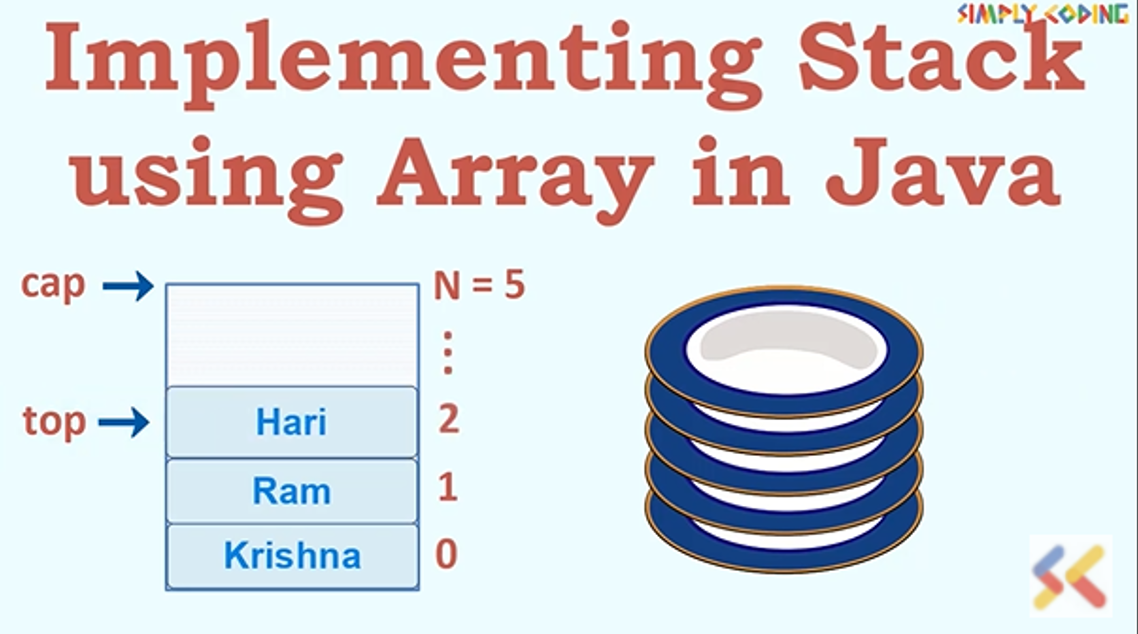
Ans. Stack is a linear data structure implemented in Last in and First out or LIFO manner. Like for example a stack of plates, where insertion and deletion happens only at one end.
Q. What is overflow and underflow situation? Or What is difference between them?
Ans.Overflow underflow Overflow refers to when one tries to push an item in stack that is full Underflow refers to when one tries to POP/delete an item from an empty stack This situation occurs when the size of the stack is fixed and cannot grow further or there is no memory left to accommodate new item This situation is when the stack is empty and still one tries to pop/delete an item
Q. What are the two major stack operations?
Ans. The two operations performed on the stack are:
- Push: Adding (inserting) new element on to the stack.
- Pop: Removing (deleting) an element from the stack.
Q. list the different operations perform on the stack?
Ans.
- Push i.e., Insertion of element in the stack
- Pop i.e., Deletion of an element from the stack
- Peek i.e., viewing topmost element without removing it
- isEmpty() i.e., checks if the stack is empty.
- Display or view all the elements in the stack.
stack operation program .
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Stack
{
String [] name;
int cap;
int top;
boolean parenthesisChecker(String s)
{
for (int i = 0; i < s.length();i++) { char c = s.charAt(i); switch (c) { case '{': case '[': case '(': push(Character.toString(c)); break; case ')': String b = pop(); if (b.charAt(0) != '(') { System.out.println(b + " UnMatched ) "); return false; } break; case ']': b = pop(); if (b.charAt(0) != '[') { System.out.println(b + " UnMatched ] "); return false; } break; case '}': b = pop(); if (b.charAt(0) != '{') { System.out.println(b + " UnMatched } "); return false; } break; default: System.out.print("Ignore "+ c); } } return true; } Stack(int size) { cap = size; name = new String[cap]; top = -1; } Stack() { top = -1; cap = 100; name = new String[cap]; } void push (String s) { if (top+1 >= cap)
{
System.out.println("Stack Overflow");
}
else
{
top++;
name[top] = s;
System.out.println("push successful");
}
}
String pop()
{
if (top < 0)
{
System.out.println("Stack Underflow");
return null;
}
else
{
String s = name[top];
top--;
System.out.println("pop successful");
return s;
}
}
boolean isEmpty()
{
return (top < 0);
}
void display()
{
for (int i = 0; i <= top; i++)
{
System.out.println(name[i]);
}
}
String peek()
{
if (top < 0)
{
System.out.println("Stack Underflow");
return null;
}
else
{
String s = name[top];
return s;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int opt = 0;
Node start = null;
Stack nameStk = new Stack();
do {
System.out.println("Enter the option: \n1 Push \n2 Pop \n3 Display \n4 Peek \n5 isEmpty \n6 Quit");
opt = input.nextInt();
switch (opt ) {
case 1:
System.out.print("Enter name to add in stack");
String data = input.next();
nameStk.push(data);
break;
case 2:
String s = nameStk.pop();
System.out.println(s);
break;
case 3:
nameStk.display();
break;
case 4:
s = nameStk.peek();
System.out.println(s);
break;
case 5:
if(nameStk.isEmpty() == true)
System.out.println("Stack Empty");
else
System.out.println("Stack Not Empty");
break;
case 7:
System.out.print("Enter string to check");
data = input.nextLine();
if(nameStk.parenthesisChecker(data) == true)
System.out.print("Matched");
else
System.out.print("UnMatched");
break;
}
} while (opt != 6);
}
}You may also like

Single Linked List Programs in Java

Constructor Programs

