
ISC Class 12 Computer Science previous year paper (2020)
- Categories Sample Papers
PART I (20 Marks)
Answer all questions
Question 1 [1 mark each]
(a) State the properties of zero in Boolean algebra.
(b) Find the complement of the following Boolean expression using De Morgan’s law:
F(P,Q,R) = P + (Q′ • R)
(c) Find the dual of: (A′ + 0) • (B′ + 1) = A′
(d) State whether the following proposition is a tautology, contradiction or a contingency:
F = (P => Q) V (Q => ~P)
(e) Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow:

(i) Name the basic gate which is represented by the diagram.
(ii) What will be the value of X when A=1 and B=0 ?
Ans.
(a) Properties of zero: A + 0 = A and A • 0 = 0
(b) F(P,Q,R) = P + (Q’ • R)
= ( P + (Q’ • R) )’
= P’ • (Q’ • R )’
= P’ • ( Q + R’)
(c) Find the dual of : (A’ + 0) • (B’ + 1) = A’
Dual = A’•1 + B’• 0 = A
(d) F = (P=>Q) V (Q=> ~P)
| P | Q | ~P | P=>Q | Q=> ~P | (P=>Q) V (Q=> ~P) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
(using laws ) : (P’ + Q) + (Q’ + P’) = 1 ( as Q + Q’ = 1)
Hence, it is a TAUTOLOGY
(e) (i) OR gate
(ii) 1
Question 2 [2 marks each]
(a) State the difference between a Binary Tree structure and a single Linked List.
(b) A matrix B[10][20] is stored in the memory with each element requiring 2 bytes of storage. If the base address at B[2][1] is 2140, find the address of B[5][4] when the matrix is stored in Column Major Wise.
(c) Convert the following infix notation to prefix form:
(X + Y) / (Z * W / V)
(d) State the best case and the worst case complexity for bubble sort algorithm.
(e) What is the significance of the keyword ‘new’ in Java? Mention the areas where it is used.
Ans.
(a) Binary Tree: A data structure in which each node has at most two sub nodes/children (left & right) Linked list: A linear collection of data elements whose order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, each element points to the next. It is a data structure consisting of a collection of nodes which together represent a sequence.
(b) Column Major Wise: B[i][j] = BA + W [ (j – lc)* row + (i – lr]
Putting the values: = 2140 + 2[ (4-1) * 10 + (5-2)]
= 2140 + 2[ 33 ]
= 2140 + 66
= 2206
(c) Infix to Prefix : (X + Y) / (Z * W / V)
= +XY / ( * Z W / V )
= +XY / /*ZWV
= /+XY/*ZWV
= /+XY/*ZWV
(d) O(n): Best case for bubble sort algorithm.
O(n2 ): Worst case for bubble sort algorithm.
(e) ‘new’ is a dynamic memory allocation operator, which is used to allot memory to non-primitive data types (example: class, array etc.).
Areas of use: To declare an object, to declare an array.
Question 3 [5 marks]
The following function check( ) is a part of some class. What will the function check( ) return when the value of (i) n=25 and (ii) n=10. Show the dry run/ working.
int check(int n)
{ if(n<=1)
return 1;
if( n%2==0)
return 1 + check(n/2);
else
return 1 + check(n/2 + 1);
}
PART – II (50 Marks)
Answer six questions in this part, choosing two questions from Section A, two from Section B and two from Section C.
SECTION – A
Answer any two questions.
Question 4 [marks in brackets ]
(a) Given the Boolean function: F(A, B, C, D) = Ʃ (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13,14).
- Reduce the above expression by using 4-variable Karnaugh map, showing the various groups (i.e. octal, quads and pairs). [4]
- Draw the logic gate diagram for the reduced expression. Assume that the variables and their complements are available as inputs. [1]
(b) Given the Boolean function: F(A, B, C, D) = π ( 3, 4, 6, 9, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 ).
- Reduce the above expression by using 4-variable Karnaugh map, showing the various groups (i.e. octal, quads and pairs). [4]
- Draw the logic gate diagram for the reduced expression. Assume that the variables and their complements are available as inputs. [1]
Ans.
(a)(1)
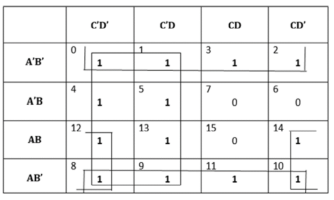
There are two octets and one quads:
Octet1 (m0+m1+m2+m3+m8+m9+m10+m11) =B′
Octet2 (m0+m1+m4+m5+m8+m9+m12+m13) = C′
Quad (m8+m10+m12+m14) = AD’
Hence F (A, B, C, D) = B’ + C’ + AD’
(2)
(b) (1)
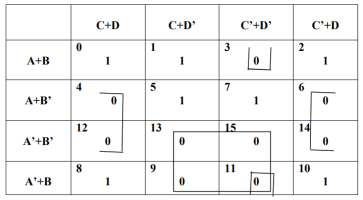
There are two quads and one pair:
Quad 1 : ( M4M6M12M14) = B’ + D
Quad 2 : ( M9M11M13M15) = A’ + D’
Pair : ( M3M11) = B + C’ + D’
Hence F(A, B, C, D) = ( B’ + D ) • ( A’ + D’ ) • ( B + C’ + D’ )
(2)

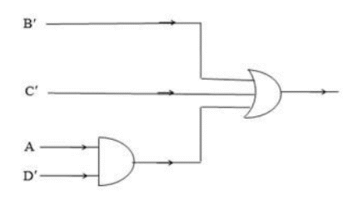
Question 5 [marks in brackets ]
(a) Draw the logic circuit diagram for an octal to binary encoder and explain its working when a particular digit is pressed. Also, state the difference between encoders and decoders. [5]
(b) Draw the circuit of a two input XOR gate with the help of NOR gates. [3]
(c) Convert the following expression to its cardinal SOP form: [2]
F(P,Q,R) = P′Q′R + P′QR + PQ′R′ + PQR′
Ans.
(a) Circuit diagram of a octal to binary encoder:

Working: It converts High Level to Low Level. Example: If input is (5)8 the output will be (101)2, i.e. binary value of 5 and so on. To convert the output signal to 1, a trigger is applied to the required gate otherwise it remains 0 as default.
An encoder is a combinational circuit which inputs 2n or fewer lines and outputs ‘n’ lines. It converts HLL to LLL e.g. octal, decimal and hexadecimal to binary
A decoder is a combinational circuit which inputs ‘n’ lines and outputs 2n or fewer lines. It converts LLL to HLL e.g. binary to octal, decimal and hexadecimal.
(b) XOR gate using only NOR gates: Expression for XOR in POS : F = (A’+B’) • (A+B)
(c) F(P,Q,R) = P’Q’R + P’QR + PQ’R’ + PQR’
= 001 011 100 110
F(P,Q,R) = ∑( 1,3,4,6 )
Question 6 [marks in brackets ]
(a) A company intends to develop a device to show the high-status power load for a household invertor depending on the criteria given below: [5]
• If Air conditioner and Geyser are on
OR
• If Air conditioner is off, but Geyser and Refrigerator are on
OR
• If Geyser is off, but Air conditioner and Water purifier are on
OR
• When all are on
The inputs are:
INPUTS
A : Air conditioner is on
G : Geyser is on
R : Refrigerator is on
W : Water purifier is on
(In all the above cases 1 indicates yes and 0 indicates no.)
Output: X [1 indicates high power, 0 indicates low power for all cases]
Draw the truth table for the inputs and outputs given above and write the SOP expression for X(A,G,R,W).
(b) Draw the truth table and derive an SOP expression for sum and carry for a full adder. Also, draw the logic circuit for the carry of a full adder. [3]
(c) Simplify the following expression using Boolean laws: [2]
F = [ (X′ + Y) • (Y′ + Z) ]′ + (X′ + Z)
Ans.
(a)
| A | G | R | W | X (OUTPUT) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
SOP Expression: X (A,G, R, W) = ∑ (6, 7, 9, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15) OR
X = A’GRW’ + A’GRW + AG’R’W + AG’RW + AGR’W’ + AGR’W +
AGRW’ + AGRW
(b) Truth Table for a Full adder:
| A | B | C | S | C0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
SOP Expression: Sum = A’B’C + A’BC’ + AB’C’ + ABC
∑ (1,2,4,7)
Carry = A’BC + AB’C + ABC’ +ABC
∑(3,5,6,7)
Circuit for carry: C0 = AB + BC + AC

(c) Simplify :[(X’+Y)•(Y’+Z)]’ + (X’+Z)
= (X’+Y)’ + (Y’+Z)’ + (X’+Z)
= XY’ + YZ’ + X’ + Z
= X’ + XY’ + Z + YZ’
= (X’+X)•(X’+Y’)+(Y+Z)•(Z+Z’)
= X’+Y’+Z +Y
= 1 as ( Y + Y’ =1)
SECTION – B
Answer any two questions.
Question 7 [ 10 marks]
Design a class Convert to find the date and the month from a given day number for a particular year.
Example: If day number is 64 and the year is 2020, then the corresponding date would be:
March 4, 2020 i.e. (31 + 29 + 4 = 64)
Some of the members of the class are given below:
| Classname | Convert |
|---|---|
| Data members/instance variables: | |
| n | integer to store the day number |
| d | integer to store the day of the month (date) |
| m | integer to store the month |
| y | integer to store the year |
| Methods/Member functions: | |
| Convert ( ) | constructor to initialize the data members with legal initial values |
| void accept( ) | to accept the day number and the year |
| void day_to_date( ) | converts the day number to its corresponding date for a particular year and stores the date in ‘d’ and the month in ‘m’ |
| void display( ) | displays the month name, date and year |
Specify the class Convert giving details of the constructor( ),void accept( ), void day_to_date( ) and voiddisplay( ).
Define a main( ) function to create an object and call the functions accordingly to enable the task.
import java.util.*;
class Convert
{
int n,d,m,y;
Convert( )
{
n=0;
y=0;
}
void accept()
{
Scanner x=new Scanner(System.in) ;
System.out.println(("Enter day number and year") ;
n=x.nextInt() ;
y=x.nextInt() ;
}
void day_to_date()
{
int a[]={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
if(y%4==0)
a[2]=29;
int s=0, c=0;
while(s<n)
s=s+a[c++];
s=s-a[--c];
d=n-s;
m=c;
}
void display()
{
String x[]={"","JANUARY","FEBRUARY","MARCH","APRIL","MAY", "JUNE","JULY","AUGUST","SEPTEMBER","OCTOBER","NOVEMBER","DECEMBER"};
System.out.print("\n Day Number: " + n);
System.out.print("\n Date: " );
System.out.print(x[m]+" " +d + "," + y);
}
static void main()
{
Convert obj =new Convert();
obj.accept( ) ;
obj.day_to_date();
obj.display();
}
}
Question 8 [ 10 marks]
Design a class BinSearch to search for a particular value in an array.
Some of the members of the class are given below:
| Classname | BinSearch |
|---|---|
| Data members/instance variables: | |
| arr[ ] | to store integer elements |
| n | integer to store the size of the array |
| Member functions/methods: | |
| BinSearch(int nn ) | |
| void fillarray( ) | |
| void sort( ) | |
| void sort( ) | searches for the value ‘v’ using binary search and recursive technique and returns its location if found otherwise returns -1 |
Define the class BinSearch giving details of the constructor( ), void fillarray( ), void sort( ) and int bin_search(int,int,int).
Define the main( ) function to create an object and call the functions accordingly to enable the task.
import java.util.*;
class BinSearch
{
int arr[];
int n;
static Scanner x=new Scanner(System.in);
BinSearch(int nn)
{
n=nn;
}
void fillarray()
{
arr=new int[n];
System.out.println("Enter "+n + " elements");
for(int i =0;i<n;i++)
arr[i]=x.nextInt();
}
void sort()
{
int t;
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)
for(int j =0;j<n-1-i;j++)
{
if (arr[j]>arr[j+1])
{
t=arr[j];
arr[j]=arr[j+1];
arr[j+1]=t;
}
}
}
int bin_search(int l,int u, int v )
{
int m=(l+u)/2;
if(arr[m]==v)
return m;
else if(l>u)
return -1;
else if (arr[m]>v)
return bin_search(l,m-1,v);
else
return bin_search(m+1,u,v);
}
static void main()
{
BinSearch obj = new BinSearch(5);
obj.fillarray();
obj.sort();
System.out.println(" location: " + obj.bin_search(0,4,20) );
}
}
Question 9 [ 10 marks]
A class Mix has been defined to mix two words, character by character, in the following manner:
The first character of the first word is followed by the first character of the second word and so on. If the words are of different length, the remaining characters of the longer word are put at the end.
Example: If the First word is “JUMP” and the second word is “STROLL”, then the required word will be “JSUTMRPOLL”
Some of the members of the class are given below:
| Classname | Mix |
|---|---|
| Data member/instance variable: | |
| wrd | to store a word |
| len | to store the length of the word |
| Member functions/methods: | |
| Mix( ) | default constructor to initialize the data members with legal initial values |
| void feedword( ) | to accept the word in UPPER case |
| void mix_word( Mix P, Mix Q ) | mixes the words of objects P and Q as stated above and stores the resultant word in the current object |
| void display( ) | displays the word |
Specify the class Mix giving the details of the constructor( ), void feedword( ), void mix_word( Mix, Mix ) and void display( ). Define the main( ) function to create objects and call the functions accordingly to enable the task.
import java.util.*;
class Mix
{
String wrd;
int len;
static Scanner x=new Scanner(System.in);
Mix()
{
wrd="";
len=0;
}
void feedword()
{
System.out.println( "Enter a word in UPPER CASE");
wrd=x.next();
len=wrd.length();
}
void mix_word(Mix P,Mix Q)
{
int s=(P.len <Q.len)? P.len:Q.len;
for(int i=0;i<s;i++)
wrd += P.wrd.charAt(i)+""+Q.wrd.charAt(i);
if (P.len > Q.len)
wrd +=P.wrd.substring(Q.len);
else
wrd +=Q.wrd.substring(P.len);
}
void display()
{
System.out.println("WORD = " + wrd);
}
static void main()
{
Mix obj=new Mix();
Mix obj1=new Mix();
Mix obj2= new Mix();
obj.feedword();
obj1.feedword();
obj2.mix_word (obj,obj1);
obj2.display();
}
}
SECTION – C
Answer any two questions.
Question 10 [marks in brackets ]
A Circular queue is a linear data structure which works on the principle of FIFO, enables the user to enter data from the rear end and remove data from the front end with the rear end connected to the front end to form a circular pattern. Define a class CirQueue with the following details:
| Class name | CirQueue |
|---|---|
| Data member/instance variable: | |
| cq[ ] | array to store the integers |
| cap | stores the maximum capacity of the array |
| front | to point the index of the front end |
| rear | to point the index of the rear end |
| Member functions/methods: | |
| CirQueue (int max) | constructor to initialize the data member cap=max, front=0 and rear=0 |
| void push(int n) | to add integer in the queue from the rear end if possible, otherwise display the message “QUEUE IS FULL” |
| int pop( ) | removes and returns the integer from the front end of the queue if any, else returns – 9999 |
| void show( ) | displays the queue elements |
(a) Specify the class CirQueue giving details of the functions void push(int) and int pop( ). Assume that the other functions have been defined. The main function and algorithm need NOT be written. [4]
(b) How is a linear queue structure different from a circular queue structure? [1]
(a)
class CirQueue
{
void push(int v)
{
if( (rear+1)% cap !=front)
{
rear = (rear + 1)% cap ;
cq[rear] =v;
}
else
System.out.println(" QUEUE IS FULL");
}
int pop()
{
if (front != rear)
{
front = ( front + 1)% cap ;
return cq[front];
}
else
return -9999;
}
}
(b) In linear queue structure the front index is always less or equal to rear index, whereas in Circular queue the front index may be greater than rear index.
Question 11 [5 marks]
An interface Data is defined with a data member and a method volume( ) which returns the volume of the implementing shape. A super class Base has been defined to contain the radius of a geometrical shape. Define a sub class CalVol which uses the properties of the interface Data and the class Base and calculates the volume of a cylinder.
The details of the members of the interface and both the classes are given below:
| Interface name | Data |
|---|---|
| Data member: | |
| double pi | initialize pi = 3.142 |
| Member functions/methods: | |
| double volume( ) | |
| Class name: | Base |
| Data member/instance variable: | |
| rad | to store the radius in decimal |
| Member functions/methods: | |
| Base(…) | parameterized constructor to initialize the data member |
| void show( ) | displays the radius with an appropriate message |
| Class name: | CalVol |
| Data member/instance variable: | |
| ht | to store the height in decimal |
| Member functions/methods: | |
| CalVol(…) | parameterized constructor to initialize the data members of both the classes |
| double volume( ) | calculates the volume of a sphere by using the formula ( pi x radius^2 x height ) |
| void show( ) | displays the data members of both the classes and the volume of the sphere with appropriate message |
Assume that the interface Data and the super class Base has been defined. Using the concept of inheritance, specify the class CalVol giving the details of the constructor(…), double volume( ) and void show( ).
The interface, super class, main function, and algorithm need NOT be written.
class CalVol extends Base implements Data
{
double ht;
CalVol(double r, double h)
{
super(r);
ht=h;
}
public double volume()
{
double x=pi * rad *rad * ht;
return x;
}
void show()
{
super.show();
System.out.println("Height= " + ht);
System.out.println("Volume= " + volume());
}
}
Question 12 [marks in brackets ]
(a) A linked list is formed from the objects of the class Node. The class structure of the Node is given below:
class Node
{
int n;
Node next;
}
Write an Algorithm OR a Method to find the product of the integer numbers from an existing linked list.
The method declaration is as follows:
void Product_Node( Node str ) [2]
(b) Answer the following questions from the diagram of a Binary Tree given below:

(i) Write the post-order traversal of the left subtree of the above structure. [1]
(ii) State the degree of the Nodes E and H. [1]
(iii) Mention the external nodes of the right subtree. [1]
Ans.
(a) ALGORITHM:
Step 1. Start
Step 2. Set temporary pointer to the first node
Step 3. Repeat steps 4 and 5 until the pointer reaches null. Display product, exit
Step 4. Accumulate the product by accessing each node
Step 5. Move pointer to the next node
Step 6. End algorithm
METHOD:
void Product_Node (Node str)
{
int s=1;
while (str!=null)
{
s=s*str.n;
str=str.next;
}
System.out.println(“Product=”+s);
}
(b) (i) G I D H F
(ii) Degree of E = 0 and Degree of H = 2
(iii) E and J
You may also like

ISC Class 12 Computer Science previous year paper (2017)

