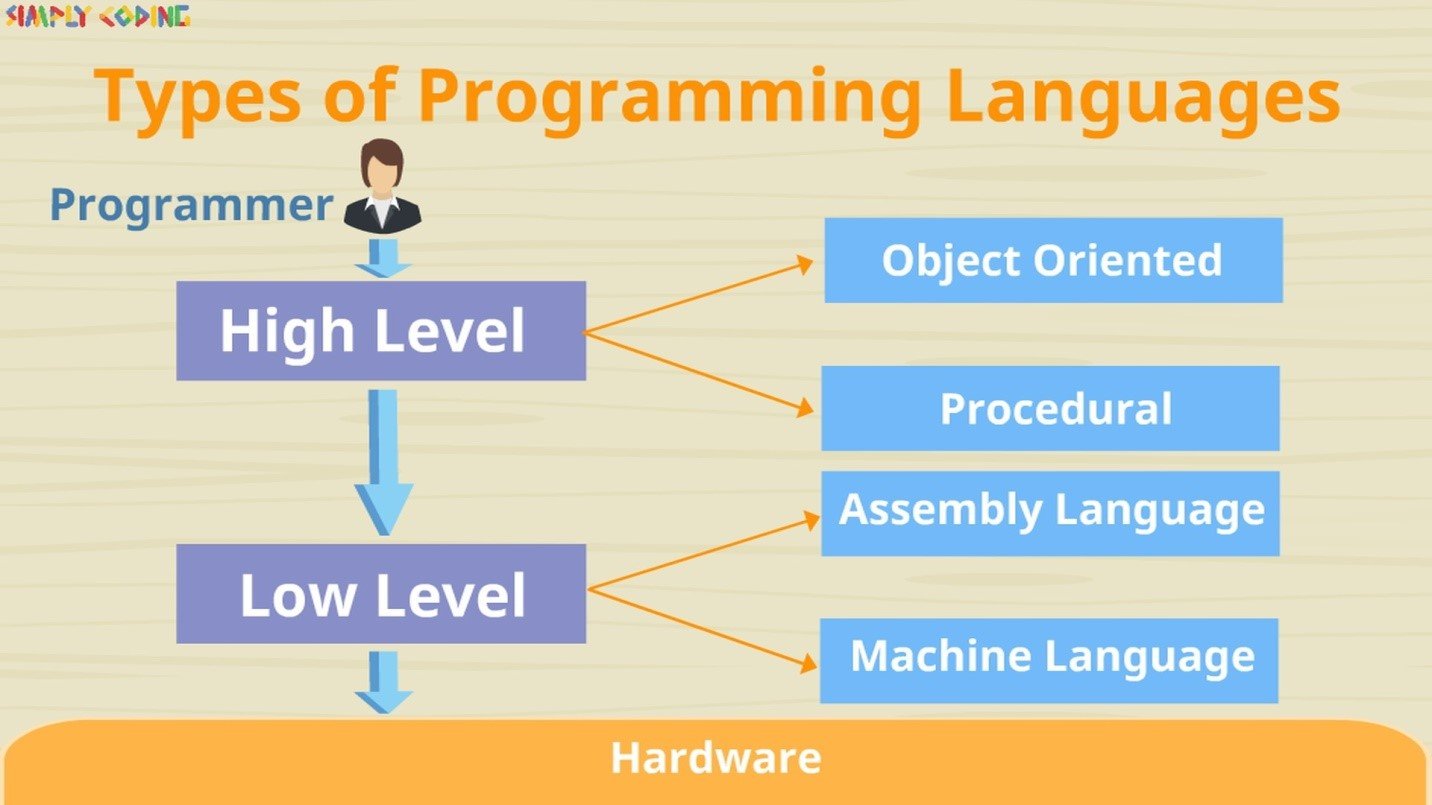
Types of Programming Languages
- Categories Java Introduction, Introduction to Java, Java
Here we are going to cover what are different types of programming languages. You can watch our video on programming languages here.
Q.1 What is Programming Language?
Ans. A programming language is an artificial language designed to communicate instructions to a machine, particularly a computer. Programming languages can be used to create programs that control the behaviour of a machine. It could be a rocket, computer or even a smart TV
Q. 2 What is Program?
Ans. A program is nothing but a list of instructions written in a programming language that is used to control the behaviour of a machine.
Q. 3 What is the difference between High Level Language and Low Level Language?
Ans.High Level Language Low Level Language Written in language which is easy to understand, code and debug Written in codes or numbers which is difficult to understand, code or debug Knowledge of hardware is not required Requires knowledge of hardware They are slower, and do not utilize CPU or memory effectively They are faster as the program can directly control CPU and memory e.g. C, C++, Java etc. e.g. MIPS, NASM etc.
Q. 4 What is Machine Language?
Ans. Machine language is the language which can directly run on CPU. They are numeric, in series of bits which is 0s and 1s representing instructions that a computer can understand. This makes it tedious and error prone to write machine code manually.
They are not portable, means a language is specific to particular type of machine only ultimately all languages need to be translated to machine language.
Q. 5 What is Assembly Language?
Ans. Assembly languages helped eliminate much of the error-prone and time-consuming machine language programming. It replaces remembering 1 and 0s with instructions which are mnemonic codes for corresponding machine language . Example it had commands like MOV, JMP, CMP , ADD etc.
Each assembly language is specific to particular computer architecture and sometimes to an operating system . E.g MIPS, NASM, x86 etc.
Q. 6 What is the difference between Procedural Language and Object Oriented Language?
Ans.
| Procedural Language | Object Oriented Language |
|---|---|
| It is top down approach | It is bottom up approach |
| It is modelled as sequence of steps or functions | It is modelled on real world as interaction between objects. |
| Program is divided into functions | Programs is divided into classes |
| Data is global so less secure | Data is hidden so is more secure |
| It does not have features such as inheritance, polymorphism, etc. | It provides features such as inheritance, polymorphism |
| e.g. C, Basic, Fortran | e.g. C++, Java, Python |
Q. 7 What is the difference between compiler and interpreter?
Ans.
| Compiler | Interpreter |
|---|---|
| The program that translate the source program or source code to machine language or low-level language at once is known as compiler. | The program that translate the source program or source code to machine language or low-level language step by step or line by line is known as interpreter. |
| Faster execution of control statements as compared to the interpreter. | Slower execution of control statements as compared to the compiler. |
| Detected errors in the program get displayed after the entire program is read by compiler. | Detected errors in the program get displayed after each instruction read by the interpreter. |
| Example: C++, Java. | Example. Python, PHP. |
Q. 8 What are advantages of object oriented programming?
Ans.
- Objects are created on real world entities.
- Complex systems of real world can be converted into software solutions.
- Objects can be easily reused in other programs due to its re-usability feature.
- Objected oriented programs focuses the developer to do extensive planning which will reduces programming flaws and better design.
- Software maintenance of the object oriented program is easier than as compared with structured oriented programming.
Q. 9 What is the difference between source code and object code?
Ans.
| source code | object code |
|---|---|
| The set of instructions and statements written by computer programmer using a programming language to find solution of problem is known as source code or program | The machine language program produced after the compilation of the source code is known as object code or object module or object program. |
| Human Readable | Machine Readable |
| Created by the programmer | Created by the Compiler |
You may also like

Questions on Encapsulation

Questions on Library classes

