
Computer Ethics – Software licenses and Open Source Software Movement.
- Categories Cyber Ethics
The term Open Source refers to software in which the source code is freely available for others to view, amend, and adapt.
We will first go through some important abbreviations which you need to know.
- FSF -Free Software Foundation. This is a Non Profit Organization created by Richard Stall man in 1985 to support Free Software movement.
- GNU’s full form is GNU’s not UNIX. This was also initiated by Richard Stallman to create a free operating system. Now it includes wide range of software and applications too.
- OSI – Open source Initiative. It is an organization which was formed in 1998 to promote open source movement. They are the ones which have given open source definition for any open source software.
- W3C -World wide web consortium. It is responsible for software standards for WWW.
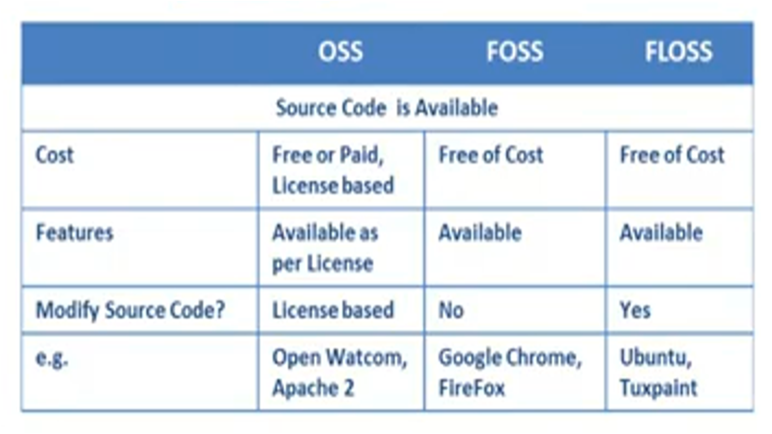
- OSS – It stands for Open Source Software. It is any Software whose source code is available to modify and redistribute. It can be free or paid software.
Open source software can either be
- FOSS means it is Free and Open Source Software.
- FLOSS which stands for Free Libre and Open Source Software. We will see the difference between them shortly.
Now on the internet there are either some set of software available where source code is not available. They can be proprietary, shareware or Freeware.
- Proprietary software, you need to purchase the license and features are unlocked only after you purchase the software. E.g. MS office, iTunes etc.
- Shareware is where the software is free only for specified period, on only few features are available for free. E.g. WinZIP or MySQL.
- Then we have Freeware. These are software where all features are available free for life. E.g. Yahoo Messenger or Adobe PDF.

Now lets see the difference between OSS, FOSS And FLOSS. When we say OSS, it can be free or paid and that is defined by the license as to what features are free and what is paid. Same source code modification is also as per license, e.g. Open Watcom or Apache. Some Software is FOSS means it is Free + Open source Here the software is free with all features but the source code modification is restricted. E.g. like Google Chrome or Firefox. If a software is FLOSS it has all the features of FOSS plus it allows you to modify the source code as well. e.g. UBUNTU or Tuxpaint
Let’s know more about licenses
License is permission granted by the holder of a copyright to another to use an original work.
Some Important Abbreviations which are linked to licenses are
- EULA: End User License Agreement.
- GPL: General Public License.
- LGPL: Lesser General Public License.
- CC: Creative Common License.
Now the license whether it is proprietary or Open Source, can be of different types
- Workstation licenses is where License is given for s use on single computer
- Concurrent use licenses is where you can install on multiple machines but no of uses should be less than licenses purchased.
- Site licenses is where you can install on any computer at a specified site
- Perpetual licenses come without an expiry date but Non-perpetual licenses “lease” the software for specific time.
- License with Maintenance offer “maintenance” along with usage.
Now we will look at different Open source licenses which are available.
Difference between GPL and LGPL
GPL is most commonly used. LGPL is more restrictive version of GPL. GPL mandates that all derivative work has to be GPL and all changes to code have to be shared. So it is mostly used for executables e.g. MySQL and LINUX uses GPL. LGPL can be used commercially and there is no requirement to share code changes. That’s why it is used mostly for software libraries like SugarCRM.
We also have BSD license which is almost same as MIT License. Both allow unlimited distribution as long as its copyright notice and disclaimer of warranty are displayed and maintained. They also restrict using its contributors for endorsements.
Apache license: Allows unlimited distribution as long as it includes clear Apache License attribution and you add modification notices to all the files modified. This license also Restricts using its contributors for endorsements. Creative Commons license is used for creative work like music, art, and websites. They are actually a set of copyright licenses where author can decide the condition of licensing

Now we will see a Case study on Licenses and open source movement
A software license is a legal agreement about an application. It is between the software producer and the end-user and is an important part of the legally binding contract between them (or rights owner) and the end-user. This is to ensure recognition of the rights of the owner on his creation. It specifies how the application may be used and defines the rights of both the producer and the user.
The open-source-software movement is a movement that supports the use of open-source licenses for some or all software, a part of the broader notion of open collaboration. Open source licenses are licenses that comply with the Open Source Definition — in brief, they allow software to be freely used, modified, and shared. These licenses can be of different type such as Workstation, Concurrent, Site, Perpetual, Non Perpetual or License with Maintenance.
Questions on Licenses and open source movement
- What is software license
- Software license allows anyone to use your product
- A software license is a legal agreement allowing consumers to use or redistribute software
- Software license does not give any rights to the end user.
- None of above
Ans. 2.A software license is a legal agreement allowing consumers to use or redistribute software
2.What is EULA?
- End-user License Agreement
- Software License Agreement
- Licensed Application End-User Agreement
- All of above
Ans. 4 All of above
3.Which of the following is not Open Source software?
- LibreOffice
- Microsoft Office
- LINUX
- MySQL
Ans.2. Microsoft Office
4.What is the difference between freeware and shareware?
- Freeware is free of cost and shareware is free for specific period of time
- Freeware features are Freely available and in shareware payment is made for some specific features
- Freeware and shareware cannot sell and make any changes
- All of above
Ans. 4. All of above
5.What is the full form of FOSS
- Free Libre and Open Source Software
- Free Libre and Open Same Software.
- Free Limited and Open Secure Software.
- Free Libre and Open Safe Software
Ans.1.Free Libre and Open Source Software
6.What is the difference between GPL And LGPL license
- GPL requires that you provide the code for all changes made to the software. LGPL does not mandate that.
- LGPL is used for software libraries, versus the execution files of GPL
- In LGPL you are permitted to keep private the proprietary material that you directly link to the software.
- All of above
Ans. 4. All of above
7.Which of the following statement is incorrect?
- Perpetual licenses come with an expiry date
- License with Maintenance offer “software assurance” along with the original license fee.
- Concurrent user licenses can be installed on more machines than number of licenses
- Site licenses permit the use of software on any computer at a specified site.
Ans.1.Perpetual licenses come with an expiry date
You may also like

Cyber Crimes and Cyber Laws


