
Cyber Ethics – IPR, Plagiarism and Digital Property Rights
- Categories Cyber Ethics, Cyber Laws, Cyber Ethics
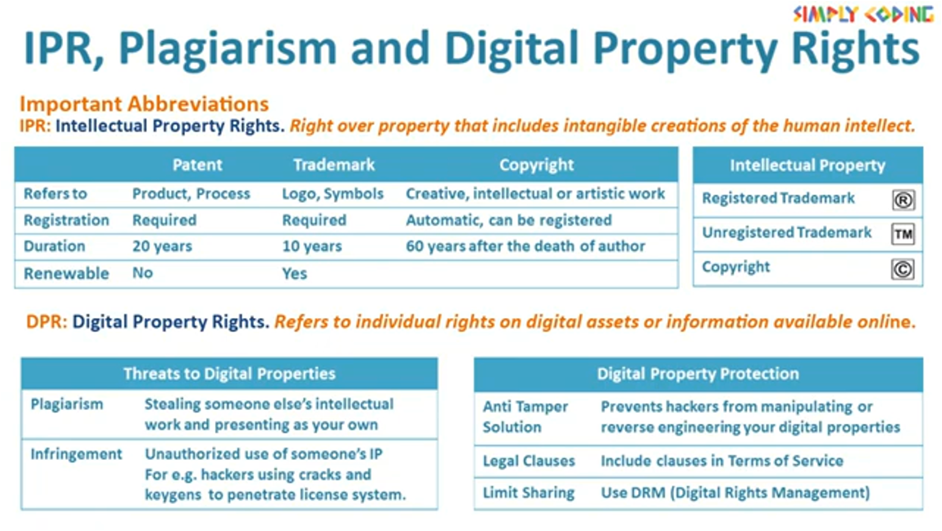
IPR stands for Intellectual property rights which are right over property that includes intangible creations of the human intellect. It includes inventions; literary and artistic works; designs; and symbols, names and images used in commerce. The most well-known types are copyrights, patents, trademarks, and trade secrets.
Patents generally apply to products and processes. You need to register it in each country where you require protection and it is valid for 20 years.
A trademark is distinctive sign, label, logo, name or slogan which identifies a product or service. It needs to be registered. The initial term is for 10 years but it can be renewed post that.
Copyright typically applies to wide range of creative, artistic or intellectual work like books, music, movies. It automatically comes into force when it is created and lasts for 60 years after the death of the author
With content moving online, now days DPR or Digital Property rights has become common. It refers to individual rights on digital assets or information available online. E.g. online accounts, e-mail accounts, photos, videos, blogs or websites etc.
There are various threats that we see on digital properties online. First of them is Plagiarism. This effectively means stealing someone else’s intellectual work and presenting as your own.
Then there is Infringement. This could be copyright, patent or trademark infringement. It is basically unauthorized use of someone’s IP for e.g. hackers using cracks and keygens to penetrate license system.
There are various steps you can take to protect your digital properties. First is to deploy Anti Tamper software or solutions. It prevents hackers from manipulating or reverse engineering your digital properties
Other option is to have a tight Term of service to be included while sharing your software so that you have a good legal backup. The third option is to limit sharing by deploying a Digital Rights management software.
Now we will see a Case Study on IPR, Plagiarism and Digital Property Rights
Cyber ethics explores appropriate and ethical behaviors related to online environments and digital media. It includes plagiarism, bullying, and hacking to name a few. Digital Property or Digital assets refers to any information about you or created by you that exists in digital form, either online or on an electronic storage device. Digital rights management (DRM) is a systematic approach for copyright protection of digital media.
Examples of digital property include: any online personal accounts, such as email and communications, social media accounts, photo and video sharing , video gaming , online storage , and websites and blogs that you may manage etc.
There are four primary types of intellectual property that can be legally protected: patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets. Each has their own attributes, requirements and costs.
Questions
- What is full form of IPR.
- Intellectual Property Rights
- Intellectual People Rights
- Intellectual Property Rate
- Intellectual Property Risk
Ans. 1.Intellectual Property Rights
2. How can we protect digital properties?
- Make digital property tamper-proof.
- Add Legal clause to use your software/digital properties.
- Limit the sharing of software code
- All of above
Ans. 4.All of above
3.Nihir managed to downloaded and watch latest movie from a suspicious site. What right of the owner has he violated
- IPR or Digital property rights
- FOSS rights
- Human right
- Public right
Ans. 1.IPR or Digital property rights
4.Ronit loves writing stories. However one day he sees someone else published his story on the net without his permission or giving him credit. What is this unauthorized use called
- Plagiarism
- Phishing
- hacking
- None of above
Ans. 1.Plagiarism
5.How can you avoid plagiarism?
- You must give credit whenever you use another person’s idea, opinion, or theory
- You should use quotations of another person’s actual spoken or written words
- You should paraphrase another person’s spoken or written words.
- All of the above.
Ans. 4.All of the above.
6.Which statement is incorrect about copyright( © )?
- It gives owner exclusive right to make copies
- It applies to creative work may be in a literary, artistic, educational, or musical form
- It can extend beyond the territory of that specific jurisdiction.
- It is valid till the lifetime of creator
Ans. 4.It is valid till the lifetime of creator
7.What is the difference between trademark( ™ or ® ) and patent.
- Trademark is protection of unique name, logos and symbols and Patent is used to protect inventions or processes.
- Trademark validity is for 10 years and Patent validity is for 20 years
- Patent can be renewed but trademark cannot
- All of above
Ans. 4. All of above
You may also like

Cyber Crimes and Cyber Laws


