Mobile Telecommunication Technologies
- Categories Emerging Trends, Networking, Computer Networks, Emerging Tech
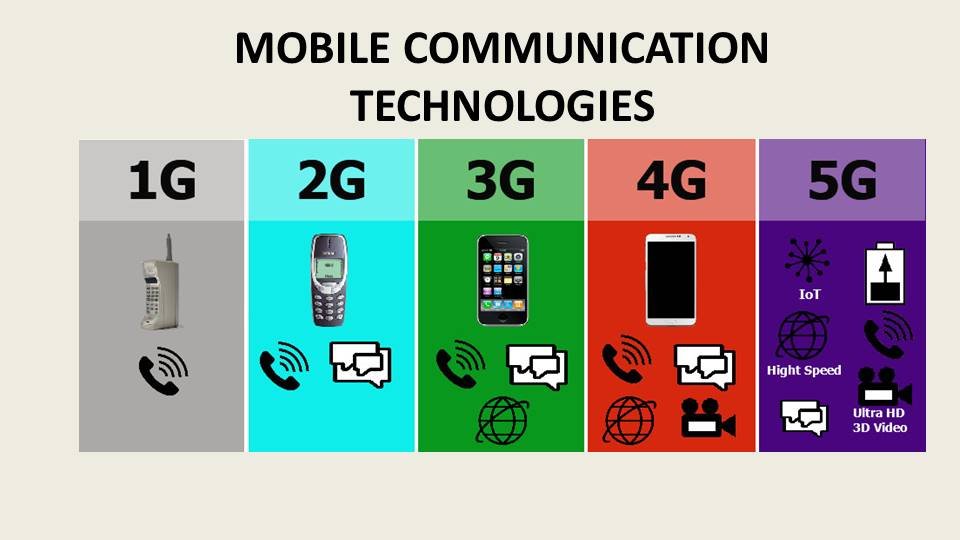
In this post, we are going to learn about different Mobile Technologies including 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G and mobile
processors.
Mobile Communication is the use of technology that allows us to communicate with others in different locations without the use of any physical connection (wires or cables).
Advantages:
- Mobile communication makes our life easier, and it saves time and effort.
- It enables the people to communicate with each other regardless of location. People can respond to emergencies relatively quickly.
- With the help of wireless technology easy accessibility to the remote areas is possible.
When we talk of 1G, 2G, 3G: the G stands for generation. Each generation has a set of network standards and technology used which defined that generation.
Let’s look at each generation one by one:
1st Generation:

The 1st generation introduced the mobile phones between the 1970s and 1980s.
It was based on analog technology called as Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS). The AMPS system was frequency modulated with a channel capacity of 30 KHz and frequency band of 824- 894MHz.
Its basic features were:
- Speed up to 2.4 kbps
- It was used only for voice services within 1 country with no roaming.
- Initial phones were large and bulky.
Other limitations of this generation were:
- It Had poor voice quality
- Battery life was poor
- Security was poor
- And it had limited capacity.
2nd generation:

Cell phones received their first major upgrade when they went from 1G to 2G
2G was launched in 1990s. Here, voice transmission moved from analog to digital signals. Technology was based on GSM i.e. Global System for Mobile Communication and CDMA.
2G capabilities were achieved by allowing multiple users on a single channel via multiplexing.
Some of its features were:
- Data speed was up to 64kbps
- It provided better quality and capacity
- Security was improved.
- It introduced services such as SMS which refers to text messages and MMS, which refers to messages with a picture or video.
- The later versions of this generation, which were called 2.5 G used GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) and 2.75G used EDGE (Enhanced data rates for GSM Evolution) networks.
Limitations of this generation were:
- It was unable to handle complex data such as videos.
- It required strong digital signals to help mobile phones work.
3rd Generation:

3G or third generation was introduced in early 2000.
These phones were required to meet IMT-2000 technical standards.
Its features were:
- It utilized Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS)
- The typical speed was 2 MBPS but
- The original technology was improved to allow data up to 14 MBPS and more by using packet switching.
- It used Wide Band Wireless Network with which clarity had increased.
- It allowed TV streaming/mobile TV/3D gaming, and so 3G phones were called Smart Phones.
- It also offered data services, high speed web and more security.
- It had new services like Global Roaming.
- IT could be used for High-speed internet service, video chatting etc.
Limitations of this generation were:
- It had High bandwidth requirement
- Fee for 3G licenses, services and expensive 3G phones were expensive.
- It was challenging to build the infrastructure for 3G
4th generation:

Next comes 4G which was introduced in 2010.
The most important 4G standards are WiMAX and LTE (long Term Evolution)
Its features were:
- I was capable of providing 10Mbps-1Gbps speed
- It expanded multimedia services and included high quality video streaming
- It offered high security and expanded multimedia services
- Low cost per-bit
Limitations of this generation were:
- Battery uses is more
- Hard to implement.
- Needed complicated hardware
5th Generation:

5G Technology stands for 5th Generation Mobile technology which started deployment in 2019. They needed to meet IMT 2020 standards.
Its features are:
- It uses New Radio (NR) frequencies, millimeter waves and Massive MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) technology.
- It offers high download speeds eventually up to 10 gigabits per second (Gbit/s)
- The main focus of 5G is to setup Wireless World Wide Web (WWWW). It is a complete wireless communication with no limitations.
- It offers Multi-media with HD Clarity
- It has large phone memory, high dialing speed and clarity in audio/video
- It allows device to device communication which will allow for new applications in internet of things (IoT) and machine to machine areas
You may also like

Switching Techniques used in computer network

Emerging Technologies – Question and Answers

