
Computer Network Devices
- Categories Computer Networks, Computer Networks
In this post we will cover various network devices. Network devices are various hardware devices that are used to connect computers, printers, etc. to a network. They are also called as networking hardware, network equipment etc. These devices help to transfer data in a fast, secure and correct way over same or different networks. Each of these devices have a specific purpose. Lets look at some of them over here.
Network interface card(NIC)
For any machine to connect to network, it first needs a Network Interface card or WIFI card.
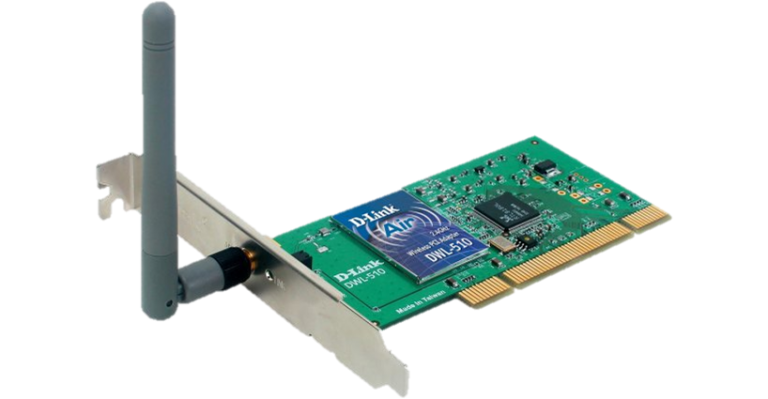
Network interface card or NIC, is also known as Ethernet card, network card, LAN card, network adapter or network adapter card (NAC) or Network Interface Unit(NIU) or Terminal Access Point (TAP). It is a physical and data link layer device used by computers to connect to Ethernet LAN and communicate with other devices on the LAN.
The earliest Ethernet cards were external to the system and needed to be installed manually. In modern computer systems, it is an internal hardware component.
The NIC manufacturer assigns a unique physical address to each NIC card. This physical address is called as MAC address or Media Access Control Address. MAC address is a 6 byte unique hardware identification number that uniquely identifies each device on a network. Because there are millions of networkable devices in existence, MAC address helps to distinguish them on the network.
Wi-Fi Card

Wi-Fi card is a card used to connect any device to the local network wirelessly. Wi-Fi is the acronym for wireless fidelity. Wi-Fi technology is used to achieve wireless connection to any network. They have a built in wireless radio and antenna. Most common cards are PIC-Express WiFi card. It is very useful if you do not have hard line network access available.
We have Wif Fi Access points which is the physical area of the network which provides internet access through Wi-Fi. IT is also called as Wi-Fi hotspot . Hotspots can be set up at home, office or any public space. Hotspots themselves are connected to the network through wires. Every access point has a range of around 120 – 150 feet for home or much larger for school or university and only devices within this range can connect to network. There can also be limit on no of computing devices that can connect to network.
So with NIC or WiFi card, your device is ready to talk to other device.
Now you need either hub, switch or router to connect to other computers.
Hub

Hub is a physical layer device which has multiple ports that are used to connect multiple computers or segments of LAN together. The data is transferred in packets to entire computer network. So when a host sends a data packet to a network hub, the hub copies the data packet to all of its ports connected to. Like this, all the ports know about the data and the port for whom the packet is intended, claims the packet.
Hubs can be passive or active. Passive hub allows the signal to be passed without any change. Active Hubs amplify the signal as it moves from one device to another. That helps to extend the range of network without using repeaters.
Disadvantages of hub is that because of its working mechanism, a hub is not so secure and safe. Moreover, copying the data packets on all the interfaces or ports makes it slower and more congested which led to the use of network switch.
Switch

Switch is more intelligent than a hub. While hub just does the work of data forwarding, a switch does ‘filter and forwarding’ which is a more intelligent way of dealing with the data packets. So, when a packet is received at one of the interfaces of the switch, it checks the destination address and transmits the packet to the correct receiver. Before forwarding, the packets are checked for collision and other network errors. This technique is called packet switching technique. The switch also maintains a list of network addresses of all the devices connected to it. Switch prevents traffic overloading in LAN.
Router

A router is the smartest or most complicated of the three. Router is mainly a Network Layer device. It can work like a switch that routes data packets based on their IP addresses It also maintains a dynamically updating routing table based on which they make decisions on routing the data packets. What it does more than switch is connecting multiple different networks together. Routers normally connect LANs with internet or other WANs together. It has the capability to repackage the data and send over another network. There are many different types of routers like WiFi router which can act as a combination router and modem, converting an incoming broadband signal from your ISP.
Differentiate between hub, switch and routers
| Sr.Nos. | Hub | Switch | Router |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hub is the least expensive, least intelligent and least complicated of the three | Switches work similarly like Hubs but in a more efficient manner | The router is smartest and most complicated out of these three. It comes in all shapes and sizes |
| 2. | It broadcasts all data to every port which may cause serious security and reliability concern | It creates connections dynamically and provides information only to the requesting port | Routers are similar like little computers dedicated for routing network traffic |
| 3. | In a network, Hub is a common connection point for devices connected to the network. Hub contains multiple ports and is used to connect segments of Lan | Switch is a device in a network which forwards packets in a network | Routers are located at gateway and forwards data packets |
Bridge

A bridge connects two or more LANs. It operates at data link layer. Bridges can however handle network that follow the same protocol.
Like a hub, a modern bridge has multiple ports, but unlike hub, when a frame arrives, the bridge extracts the destination address (for Ethernet, it is 48 bit) from the frame header and looks it up in a table to see where to send the frame.
The bridge only outputs the frame on the port where it is needed and can forward multiple frames at the same time.
Filtering, forwarding and blocking of frames are functions of bridges.
Bridges offer much better performance than hub
Gateway

Gateway is a network device used to connect two or more dissimilar networks. That is networks that use different protocols. It establishes an intelligent connection between a local network and an external network. A gateway usually is a computer with multiple NICs connected to different networks. At home it could be the ISP which connects your computer to internet.
For a large enterprise, this computer can also act as proxy server, firewall or malware protection.
Repeater

In addition network also needs repeaters. Repeater are used to extend transmissions so that the signal can cover longer distances or be received on the other side of an obstruction. It increases the power of a signal and retransmits it.
A gateway can also be configured completely using software. As networks connect to a different network through gateways, these gateways are usually hosts or end points of the network.
Modem

Modem is a device that enables a computer to send or receive data over telephone or cable lines. The data stored on the computer is digital whereas a telephone line or cable wire can transmit only analog data.
The main function of the modem is to convert digital signal into analog and vice versa. Modem is a combination of two devices − modulator and demodulator. The modulator converts digital data into analog data when the data is being sent by the computer. The demodulator converts analog data signals into digital data when it is being received by the computer.
Modem can be categorized in several ways like direction in which it can transmit data, type of connection to the transmission line, transmission mode, etc.
Depending on direction of data transmission, modem can be of these types −
- Simplex− A simplex modem can transfer data in only one direction, from digital device to network (modulator) or network to digital device (demodulator).
- Half duplex− A half-duplex modem has the capacity to transfer data in both the directions but only one at a time.
- Full duplex − A full duplex modem can transmit data in both the directions simultaneously.
You may also like

Communication Channels

Mobile Telecommunication Technologies

